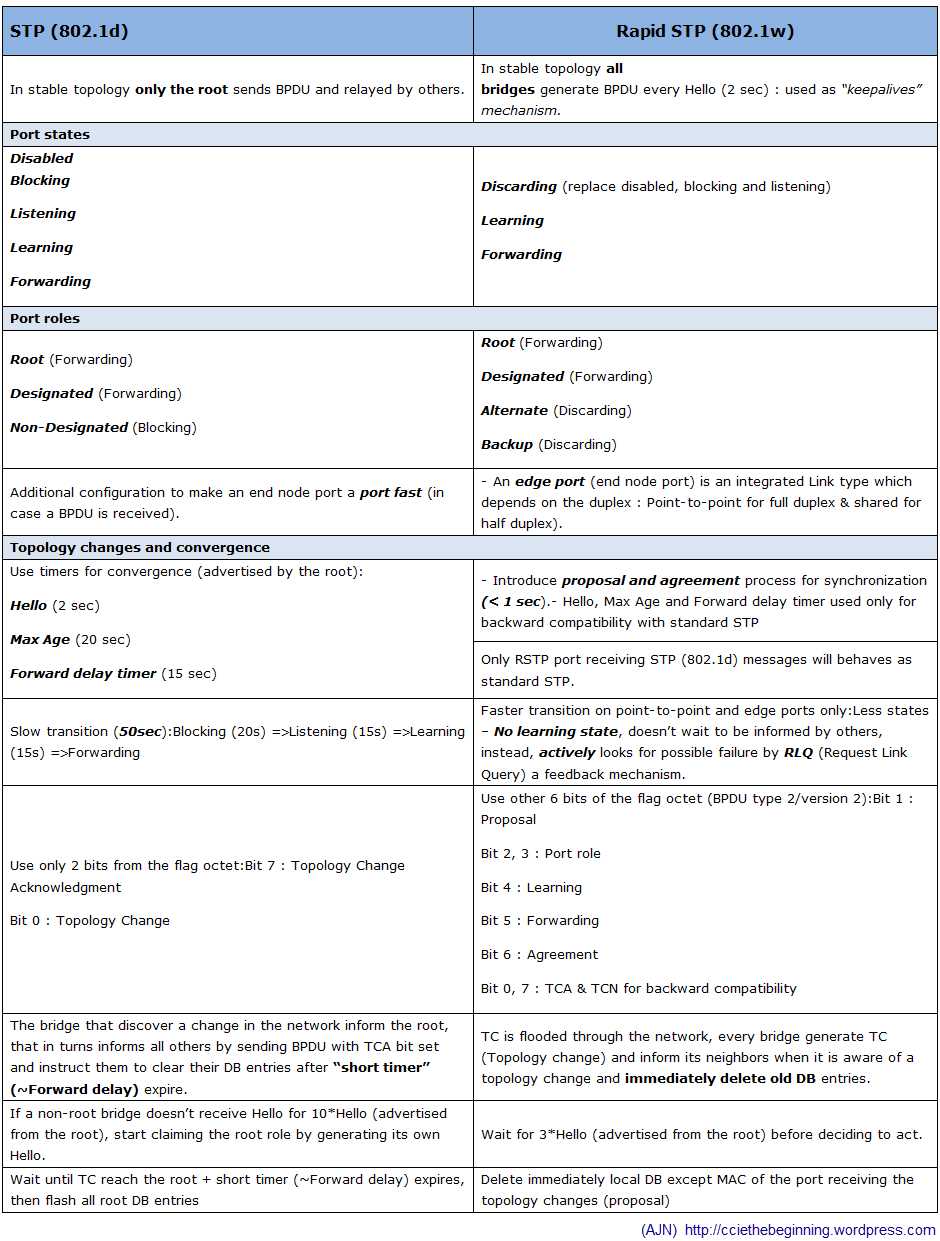
I am sure most of you computer geeks out there knows about the Spanning Tree Protocol and how it works. So the basics here just for a heads up. STP is a network protocol standard set by IEEE. The purpose of Spanning Tree is to prevent loops in the LAN and to select the fastest network links, if there are redundant links available in the network. Naturally the first question pops in your mind would be “What routers are doing then?”. Well routing protocols helps devices to route between different networks on Layer-3 network. But you should know that it’s not a routing protocol but has similar not identical functions for the Data Link Layer (Layer-2).
Configuring Spanning Tree on Cisco: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/lan/catalyst4000/8-2glx/configuration/guide/spantree.pdf
Now the part comes why it’s used to control network loops. Because the ports are put into ready-state, and these are best ports. A real usage is that when a new switch is introduced in the network, all the port states are recalculated by the algorithm. The port states are also gets recalculated when the port states are down as well.
Here is a Cisco Layout for the States: https://learningnetwork.cisco.com/thread/34579
IEEE 802.1D Path Cost Parameter Values
| Link Speed | Recommended Value |
Recommended Range |
Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4 Mbps | 250 | 100-1000 | 1-65535 |
| 10 Mbps | 100 | 50-600 | 1-65535 |
| 16 Mbps | 62 | 40-400 | 1-65535 |
| 100 Mbps | 19 | 10-60 | 1-65535 |
| 1 Gbps | 4 | 3-10 | 1-65535 |
| 10 Gbps | 2 | 1-5 | 1-65535 |
IEEE 802.1t Path Cost Parameter Values
| Link Speed | Recommended Value |
Recommended Range |
Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 Mbps | 2.000.000 | 200.000-20.000.000 | 1-200.000.000 |
| 100 Mbps | 200.000 | 20.000-2.000.000 | 1-200.000.000 |
| 1 Gbps | 20.000 | 2.000-200.000 | 1-200.000.000 |
| 10 Gbps | 2.000 | 200-20.000 | 1-200.000.000 |
| 100 Gbps | 200 | 20-2.000 | 1-200.000.000 |
| 1 Tbps | 20 | 2-200 | 1-200.000.000 |
| 10 Tbps | 2 | 1-20 | 1-200.000.000 |
Default Observed on Cisco Switches
| Speed | Port Cost | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| 10 Mbps | 100 | Ethernet |
| 20 Mbps | 56 | EtherChannel |
| 30 Mbps | 47 | EtherChannel |
| 40 Mbps | 41 | EtherChannel |
| 50 Mbps | 35 | EtherChannel |
| 54 Mbps | 33 | 802.11 wireless |
| 60 Mbps | 30 | EtherChannel |
| 70 Mbps | 26 | EtherChannel |
| 80 Mbps | 23 | EtherChannel |
| 100 Mbps | 19 | Fast Ethernet |
| 200 Mbps | 12 | Fast EtherChannel |
| 300 Mbps | 9 | Fast EtherChannel |
| 400 Mbps | 8 | Fast EtherChannel |
| 500 Mbps | 7 | Fast EtherChannel |
| 600 Mbps | 6 | Fast EtherChannel |
| 700 Mbps | 5 | Fast EtherChannel |
| 800 Mbps | 5 | Fast EtherChannel |
| 1 Gbps | 4 | Gigabit Ethernet |
| 2 Gbps | 3 | Gigabit EtherChannel |
| 10 Gbps | 2 | 10G Ethernet |
| 20 Gbps | 1 | 20G EtherChannel |
| 40 Gbps | 1 | 40G EtherChannel |